What does the European Court of Human Rights’ first climate change decision mean for climate policy?

The European Court of Human Rights has issued its first ever comprehensive decision in a climate litigation case – heard in a Swiss court. Catherine Higham, Isabela Keuschnigg, Tiffanie Chan and Joana Setzer explore how effective the type of regulatory framework envisioned by the Court can be in accelerating credible climate action across Europe.
On 9 April the European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR) issued its first ever comprehensive decision in a climate litigation case. The judges of the Court’s Grand Chamber found that Switzerland was in breach of its positive obligations to protect the health, well-being and quality of life of Swiss citizens from the impacts of climate change. This violation was attributed to the Swiss government’s failure to implement the robust regulatory framework necessary for fulfilling its commitment to reduce emissions as set out in the Paris Agreement.
As the dust begins to settle on this case, the critical question in the minds of many is what implication the judgment will have for how Switzerland and the 45 other signatories of the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR) now address climate change.
Could this ruling catalyse the rapid cross-cutting action that is urgently needed?
Firstly, this is a question of compliance: will Switzerland and the other ECHR signatories find the judgment a compelling reason to amend their climate laws in line with the guidance given by the court? Most commentators have focused on this element. While there appears to be a general consensus that the ruling will be “transformative”, some have treated it more cautiously. In particular, while the case is expected to have “knock-on” effects on law and policymaking at the domestic and international levels, the extent of these impacts will take time to crystallise. Some researchers argue that with its ruling the Court has merely set a “minimum standard” and thus they question whether it will lead to ECHR signatories significantly tightening their climate laws.
But importantly, this is also about effectiveness: can the type of regulatory framework envisioned by the Court drive countries to meet their legislative climate commitments? We focus our analysis below on this aspect, seeking to assess how effective the type of regulatory framework envisioned by the Court can be in accelerating credible climate action.
A domestic regulatory framework aligned with human rights obligations
In its judgment, the Court set out a series of minimum requirements that a domestic regulatory framework must meet to align with human rights obligations. These are firmly grounded in the architecture of the Paris Agreement, reflecting global practices in climate governance and strong scientific foundations.
Climate framework laws have emerged as a prominent tool to drive domestic climate action, including establishing regulatory frameworks. To date, 59 countries, including 25 ECHR signatories, have enacted climate framework laws. As well as setting the strategic direction for national climate policies, these laws often include long-term climate objectives: for example, 17 countries’ laws contain net zero or climate neutrality targets.
The scope of these laws, however, varies significantly. Some countries, like Nigeria, set up inter-ministerial coordination bodies to prepare national climate action plans designed to meet targets, whereas others like Canada mandate interim targets or carbon budgets based on the advice of independent expert advisory bodies. In some cases, like Japan, legislation separately addresses mitigation and adaptation efforts. At times, countries also establish domestic governance processes across multiple laws, executive policies or through informal processes.
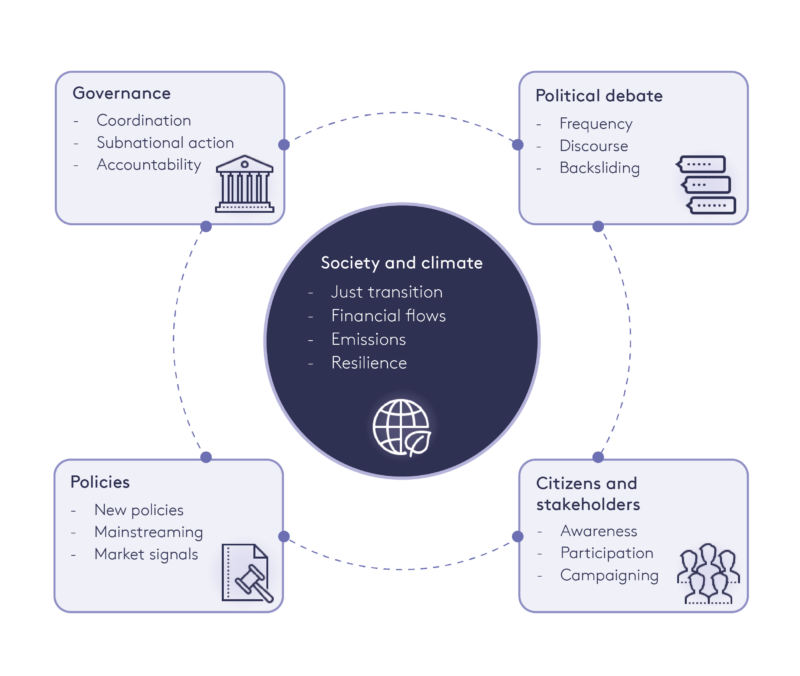
Unfortunately, when it comes to understanding the impact of such climate framework laws, empirical evidence remains limited, particularly regarding how impacts might vary across different socioeconomic and political contexts. However, research conducted by the Grantham Research Institute into the impacts of climate framework laws in the UK, and most recently in Germany, Ireland and New Zealand, has uncovered varied impacts across five key areas (see Figure 1). These findings indicate that the most significant impacts of climate framework laws are observed in the areas of governance and political debate.
Figure 1. Impacts of climate framework laws
Mapping the Court’s minimum requirements against the building blocks of effective climate laws
The Court’s specified set of minimum requirements for a State’s regulatory framework on climate change (paragraph 550 of the judgment) align closely with what our research identifies as the core building blocks of effective climate framework laws – see Table 1 below. Not only do these elements of climate laws have the most direct influence: they also lead to the most significant impacts. Our research shows that these building blocks directly contribute to the robustness of regulatory frameworks, ensuring that climate action is both ambitious and grounded in scientific evidence.
Table 1. The ECtHR’s minimum requirements mapped against our identified building blocks for effective climate framework laws
| EHtCR’s minimum requirements | Core building blocks of climate laws |
| Adoption of general measures specifying targets for achieving carbon neutrality and the remaining carbon budget for that timeline, or equivalent, in line with national and/or global climate change mitigation commitments. Intermediate emissions reduction targets and pathways. | Establishing targets and carbon budgets. |
| Evidence of compliance with the relevant targets. Updating the relevant targets with due diligence in line with the best available science. | Setting standards for reporting, assessment and review of progress. |
| Acting in good time and appropriately and consistently when implementing the laws and measures. | Mandating public sector actions. Shaping planning and policy processes. |
The similarities between the Court’s stipulated requirements for regulatory frameworks and the building blocks that make climate framework laws most effective suggest that the approach required by the Court could have significant positive impacts.
However, while these components are crucial, they may not be sufficient on their own to catalyse rapid and enduring change. Although many climate framework laws mandate public consultation, the specifics of these processes are often imprecisely defined, leaving uncertainty about how public participation, stakeholder engagement and deliberative processes are to be continuously or formally integrated into an institutional framework. This integration is vital for ensuring public acceptance of climate policies.
The Court addressed this need in paragraph 554 of its judgment, underscoring the importance of public participation and access to information in developing climate policies. The extent to which this aspect of the judgment will influence future legislative practices and improve the inclusivity and effectiveness of climate governance remains an open question.
Helpful guidance from the Court – but ultimately it comes down to political will
Our research also highlights that there are significant challenges to implementing climate framework laws: in particular, without sustained political will, enforcement becomes very difficult. Another recurring issue is the absence of stringent penalties for non-compliance, which undermines the credibility of these laws and poses risks to democratic accountability. Litigation, while a last resort, can strengthen both administrative and political accountability for fulfilling climate commitments. The KlimaSeniorinnen ruling highlighted significant gaps in Switzerland’s regulatory framework and its failure to meet previous emissions targets, underscoring the judiciary’s role in holding states accountable for their climate obligations.
The European Court of Human Rights has set out clear directions for member states to follow to align their climate policies with human rights obligations. Domestic legislators across Europe must give these requirements serious consideration to ensure their climate laws not only meet these minimum standards but also effectively contribute to global climate goals. This is imperative for both environmental sustainability and the protection of fundamental human rights that climate change is affecting.

