Asymmetric industrial energy prices and international trade
External Links
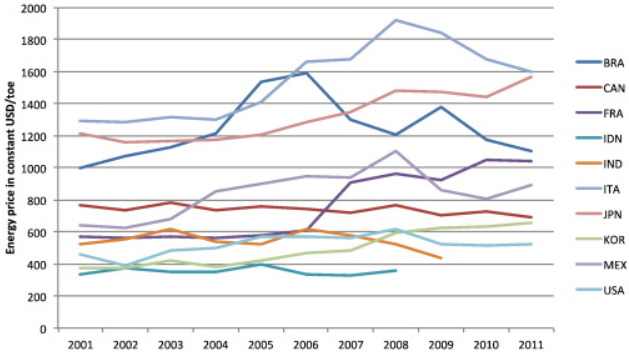
This paper measures the response of bilateral trade flows to differences in industrial energy prices across countries. Using a rich panel dataset with 42 countries, 62 manufacturing sectors over 16 years (1996–2011) and covering 60% of global merchandise trade, we estimate the short-run effects of sector-level energy price asymmetry on trade. We find that changes in relative energy prices have a statistically significant but very small impact on imports. On average, a 10% increase in the energy price difference between two country-sectors increases imports by 0.2%. The impact is larger for energy-intensive sectors. Even in these sectors, however, the magnitude of the effect is such that changes in energy price differences across time explain less than 0.01% of the variation in trade flows. Simulations based on our model predict that a €40–65/tCO2 price of carbon in the EU ETS would increase Europe’s imports from the rest of the world by less than 0.05% and decrease exports by 0.2%.
Energy Economics, December 2014

